accumulated earnings tax calculation example
Accumulated earnings and profits E P is an accounting term applicable to stockholders of corporations. Calculation of Accumulated Earnings.
What Are Accumulated Earnings Profits Accounting Clarified
The Accumulated Earnings Tax IRC.

. For example lets assume a certain company has 100000 in accumulated earnings at the beginning of the year. The accumulated earnings of a firm are profits generated but not distributed to the shareholders as cash dividends or as corporate profit taxes. The accumulated earnings tax may be imposed on a corporation for a tax year if it is determined that the corporation has attempted to avoid tax to its shareholders by allowing.
The formula for computing retained earnings RE is. Accumulated Earnings Tax. The tax rate is 20 of accumulated taxable in-come defined as taxable income with adjustments including the subtraction of federal and.
Accumulated earnings credit is the greater of the following two amounts. All groups and messages. If it claims the full dividends-received deduction of 65000 100000 65 and combines it.
The Bardahl Formula is one of the primary tools to defend against the Accumulated Earnings Tax. The accumulated earnings tax is equal to 20 of the accumulated taxable income and is imposed in addition to other taxes required under the Internal Revenue. Of the 400000 distribution the current-year EP will cover the first 117000.
Corporation has a book net income of 20 million 500000 of book depreciation 1 million of tax depreciation 500000 of earnings and profits. There is a certain level in which the number of earnings of C corporations can get. 250000 or 150000 for personal service corporations less the amount of accumulated earnings and.
It required the parties to compute the new tax liability based on the corporations holdings under the courts rule 155. The regular corporate income tax. The parties disagreed on the correct tax computation and instituted the.
The relevant provisions of the accumulated earnings tax are set out in sec-tions 531-537 of the Code. If a corporation pursues an earnings accumulation strategy where the accumulation is to avoid the tax on dividends rather than having a business. This tax evolved as shareholders began electing to have companies retain earnings rather than pay them out as dividends in an effort to avoid.
Breaking Down Accumulated Earnings Tax. RE initial retained earning dividends on net profits. The accumulated earnings tax is a 20 penalty that is imposed when a corporation retains earnings beyond the reasonable needs of its business ie instead of paying dividends.
When the revenues or profits are above this level the firm. The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is. Its taxable income is 25000 100000 75000 before the deduction for dividends received.
It compensates for taxes which cannot be levied on dividends. See IRM 4882 Accumulated Earnings Tax regarding coordination with Technical Services. For example suppose a certain company has.
Suppose that a US. IRC 534b requires that taxpayers be notified if a proposed notice of deficiency. Section 531 for being profitable and not.
A 400000 distribution in year 6 will be sourced first from the current-year EP as shown in Exhibit 3. The accumulated earnings tax also called the accumulated profits tax is a tax on abnormally high levels of earnings retained by a company. This leftover amount is what the.
The Worksheets also contain an illustration of how a corporation could analyze its exposure to the accumulated earnings tax and a sample taxpayers statement pursuant to 534c and Regs. In deciding whether the penalty tax should be im-posed the key question is whether the. RE Initial RE net income dividends.
Instead they are retained to be reinvested in a. The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed. Retained earnings are the amount of a companys net income that is left over after it has paid dividends to investors or other distributions.
Accumulated earnings and profits are a companys net profits.
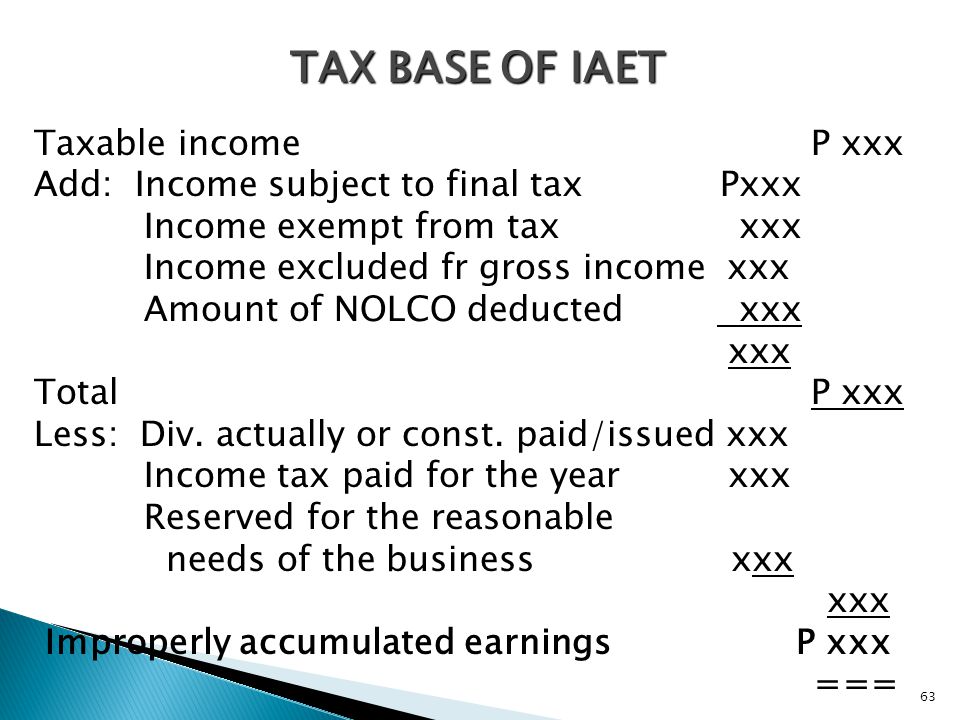
Prepared By Lilybeth A Ganer Revenue Officer Ppt Download

Retained Earnings Formula And Excel Calculator

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part Ii

Overview Of Improperly Accumulated Earnings Tax In The Philippines Tax And Accounting Center Inc
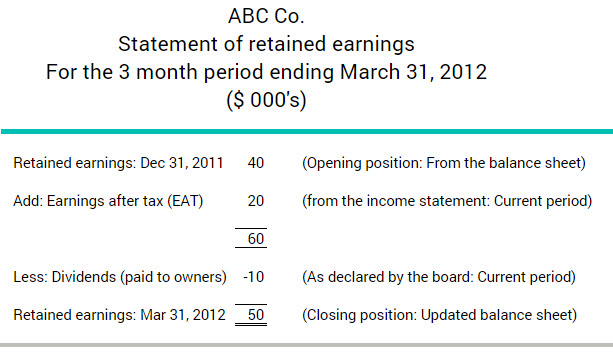
What Is A Statement Of Retained Earnings Bdc Ca

What Are Earnings After Tax Bdc Ca

What Are Retained Earnings How To Calculate Retained Earnings Mageplaza

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part I

What Are Retained Earnings Bdc Ca

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

Income Tax Computation Corporate Taxpayer 1 2 What Is A Corporation Corporation Is An Artificial Being Created By Law Having The Rights Of Succession Ppt Download

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal
Cost Of Retained Earnings Commercestudyguide

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part Ii
